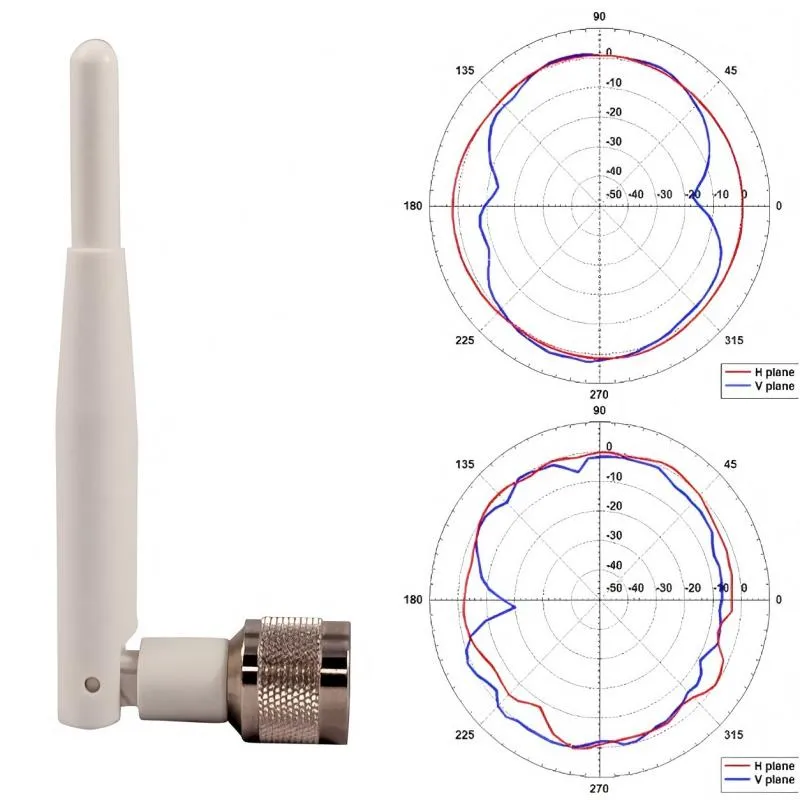
5V to 12V Boost Converter Design in Practice
Designing a 5V to 12V boost converter sounds straightforward until you build one and watch the waveform ripple across your scope. Real boards expose trade-offs that datasheets rarely warn about — efficiency, thermal margin, and part sourcing. From the veteran MC34063 to today’s integrated synchronous ICs, the path is full of judgment calls that decide whether your converter runs cool or cooks itself.